

The Canon EOS R10 on the microscope: a mirrorless system camera that scores high marks for its price-to-performance ratio
The EOS R10, Canon’s new entry-level model in the mirrorless series, featuring Canon’s familiar APS-C sensor and a large RF mount, was launched in summer 2022. Until then, this type of lens mount had been reserved for Canon’s expensive full frame cameras. However, the EOS R10 is designed as an entry-intermediate model that is the mirrorless successor to the popular EOS 850D. The price tag (body only) is around EUR 950 (as of October 2022).
With our LM microscope adapters, the EOS R10 can be attached to virtually any microscope – either via the phototube or the eyepiece tube.

Key specifications:
- 25 MP APS-C (22.5 mm x 15.0 mm) CMOS imaging sensor
- High-speed continuous shooting at up to 23 fps with electronic (silent) shutter and up to 15 fps with mechanical shutter
- ISO range of 100 to 51,200
- Movie recording frame size (pixels) and frame rate: 3,840 x 2,160 (4K UHD) up to 60p
- Ability to record video past the usual 30-minute clip limit
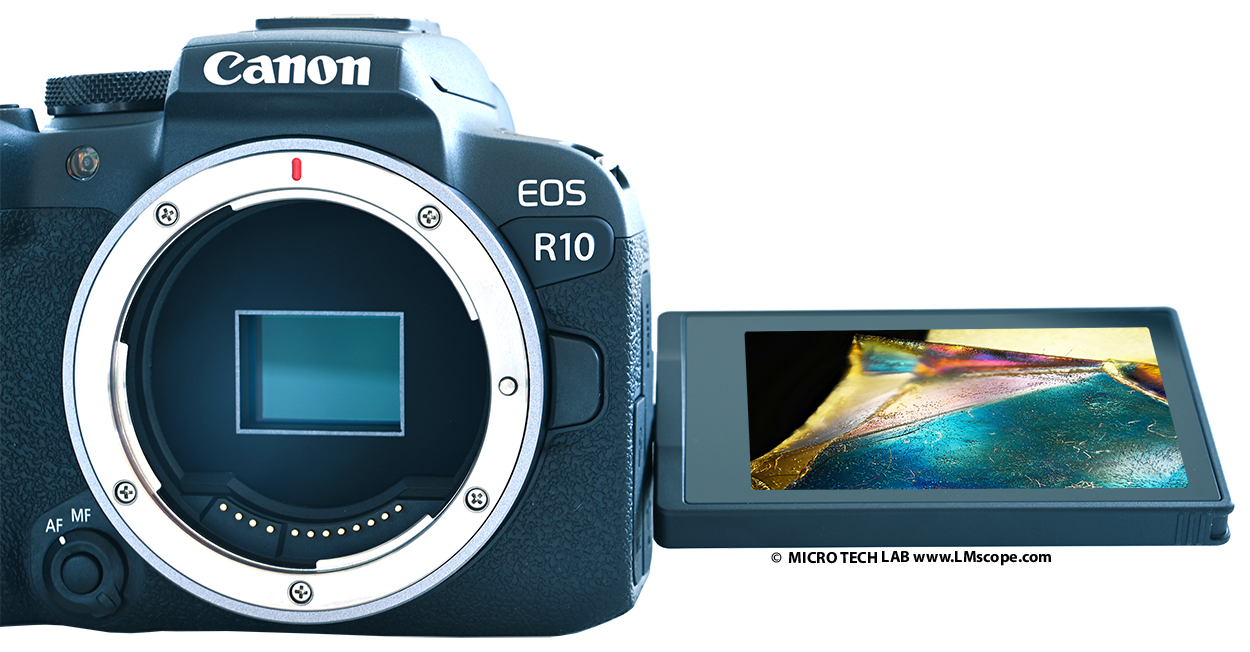
- 3.0'' TFT LCD fully-articulating display
- Shutter speeds between 1/16,000 and 30 seconds
- SD (UHS-II) card slot housed next to the battery at the bottom of the camera
- Electronic image stabiliser
- USB 2.0 type C for data transfer, charging and continuous power
- HDMI micro out terminal (type D) to display the live image on an external monitor
- Built-in Wi-Fi (wireless LAN), Bluetooth technology
- Weight: 429 g (body only)
- 4K and Full HD time lapse at 25 and 30 fps
- Compatible with LP-E17 battery pack
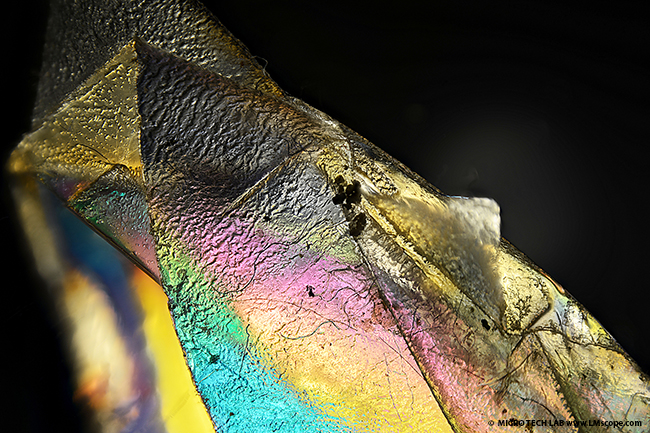
Demo photo: plastic film photographed with the EOS R10 combined with an LM adapter with integrated polarising filter
We really liked how the EOS R10, nicknamed the little sister to the EOS R7, performed on the microscope. With our LM adapter systems, it can be attached to the phototube of almost any microscope in a few easy steps. Our adapter solutions with high-quality plan achromatic precision optics are designed for professional use and deliver the best possible image quality – even with lower-priced cameras like the EOS R10.
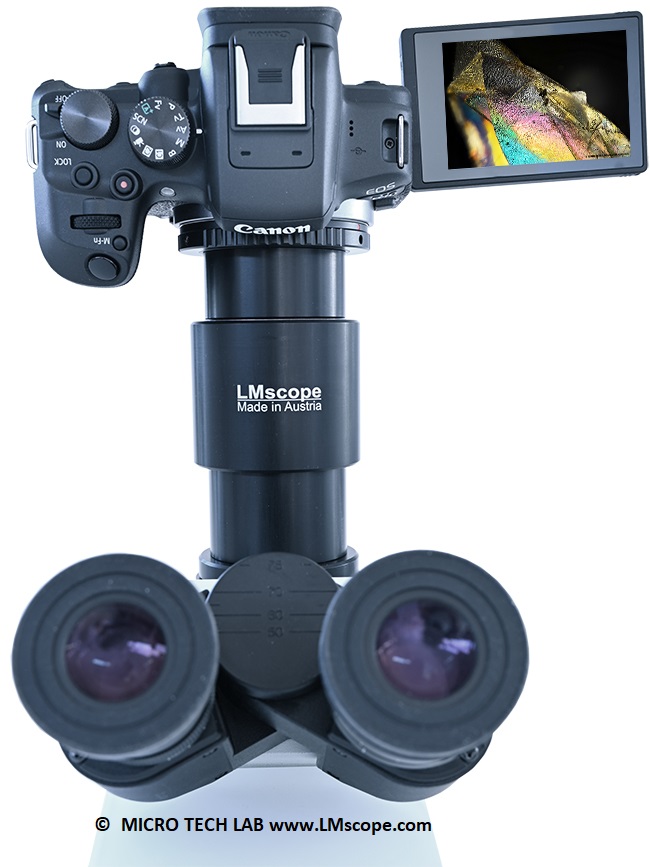

If the microscope doesn’t have a phototube, the camera can also be attached to the eyepiece tube by removing one eyepiece and putting the camera-adapter combination into its place.
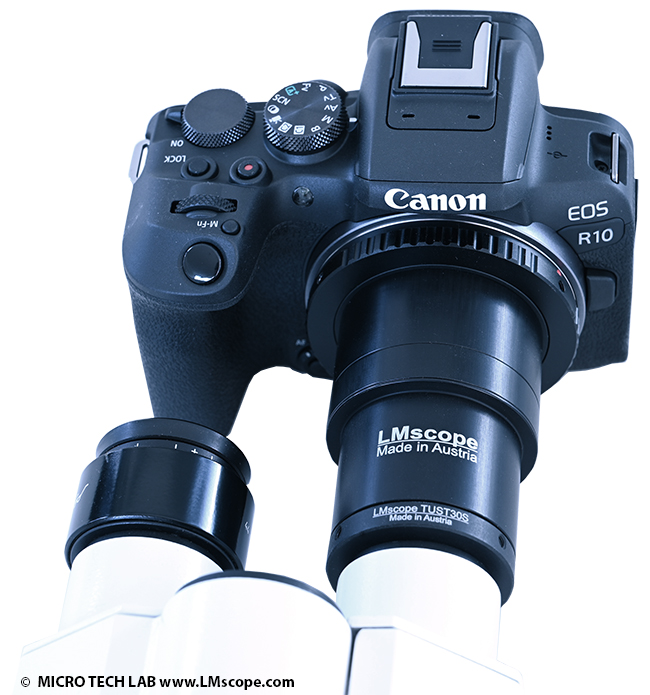

Operate the Canon EOS R10 mid-range camera on the eyepiece tube with 23.2mm or 30mm
You often don’t even need to purchase an expensive professional camera to get excellent image quality, because the limiting factor in photomicrograph is usually the microscope. At a starting price of around EUR 950 (October 2022), the EOS R10 falls into the lower price segment of mid-range cameras currently on the market. The EOS R10 (same as the R7) is the first APS-C camera to feature Canon’s current RF mount, which has different dimensions than the standard EF lens mount on Canon DSLRs.
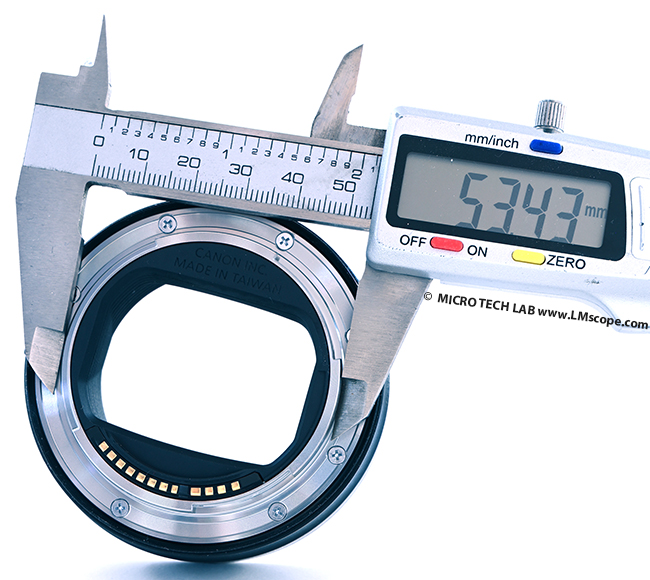

The sensor has a resolution of 25 megapixels and is very fast. With a maximum shutter speed of 1/16,000 (electronic shutter), it is possible to effectively freeze fast moving objects while in motion. The R10 supports up to 15 fps continuous shooting, which is truly impressive considering the camera’s relatively moderate price tag.
In video mode, the user can choose between 4K format (with 60 fps) and Full HD with up to 120 fps. Unlike previous models, the R10 does not have a time limit for video recording – the only constraints are battery and memory card capacity. And even these are easy to circumvent: using a USB cable, videos can simply be sent directly to the computer and stored there. Of course, a USB 3.1 port would be preferable for fast data transfer, but the built-in USB 2.0 port is usually sufficient enough for our needs. Although it is also possible to supply continuous power to the camera via the USB cable, we nevertheless recommend using an external charging unit. The LP-E17 battery type has been used by Canon for years, and there are many dummy batteries available that won’t burn a hole in your pocket. You can get them on the internet or in photography stores.
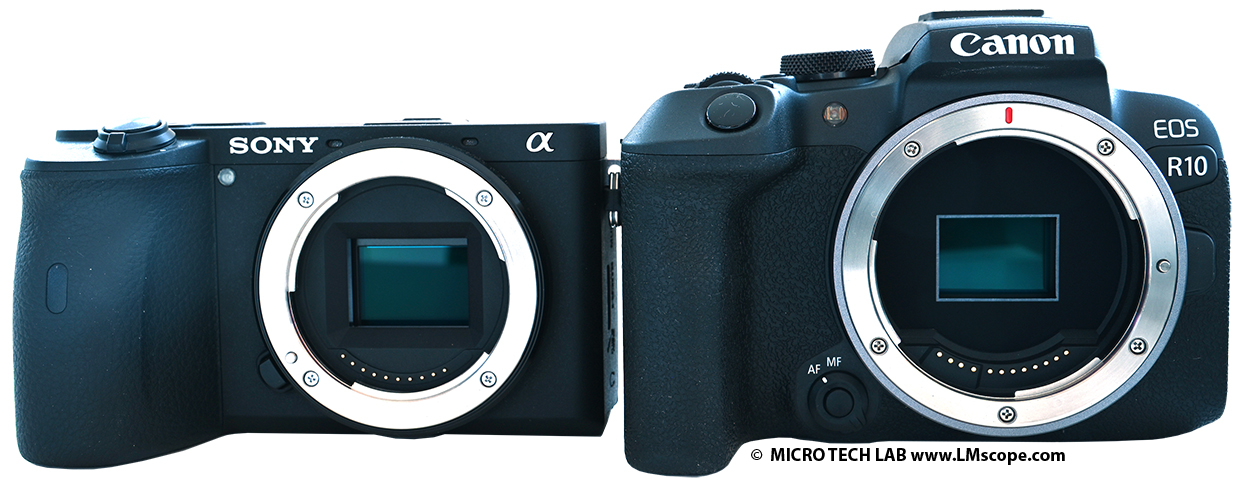
The comparison with the competitor model, the Sony Alpha 6600, which also uses an APS-C sensor, shows the compact design of both cameras:

The camera can be controlled either via a cable connection (USB) or a wireless network (WLAN/Wi-Fi). We generally recommend controlling the camera remotely from a PC/Mac. The Canon EOS Utility software is included in the price of the R10 and does not need to be purchased separately. The software is very intuitive and has a clear and structured layout. Installing it on the computer is easy:
Connect the camera to the computer with a USB cable and start the software. The computer recognizes the camera.
Select the “Remote Shooting” option:
The Live View is displayed on the computer screen:
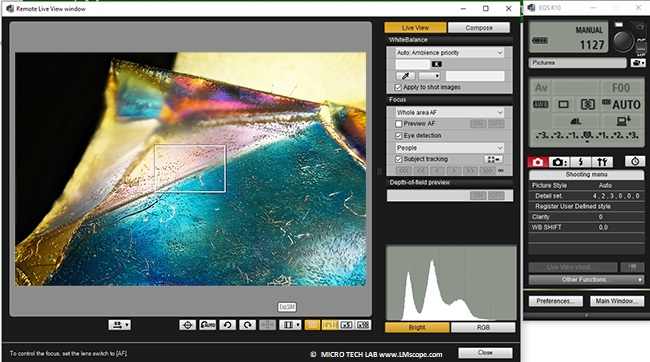
Now, different settings can be configured, for example ISO speed:
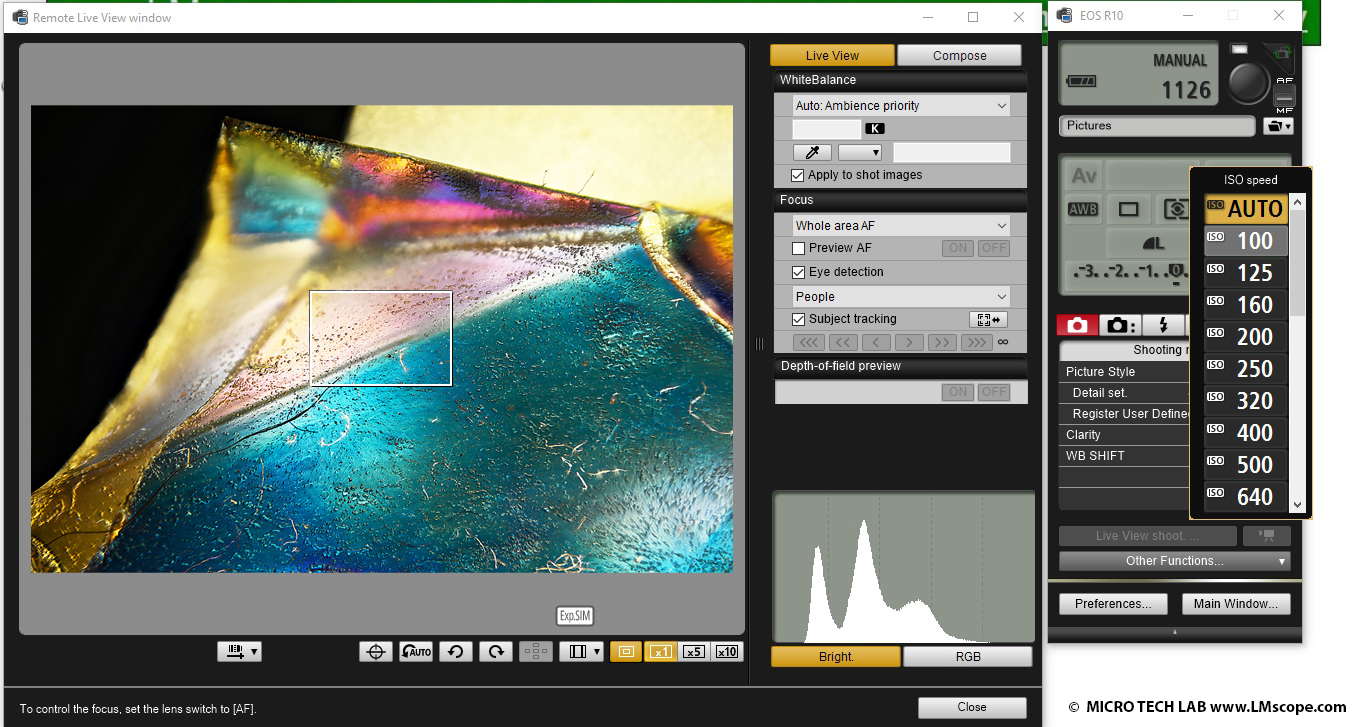
Image above: minimum ISO (100); image below: high ISO speed
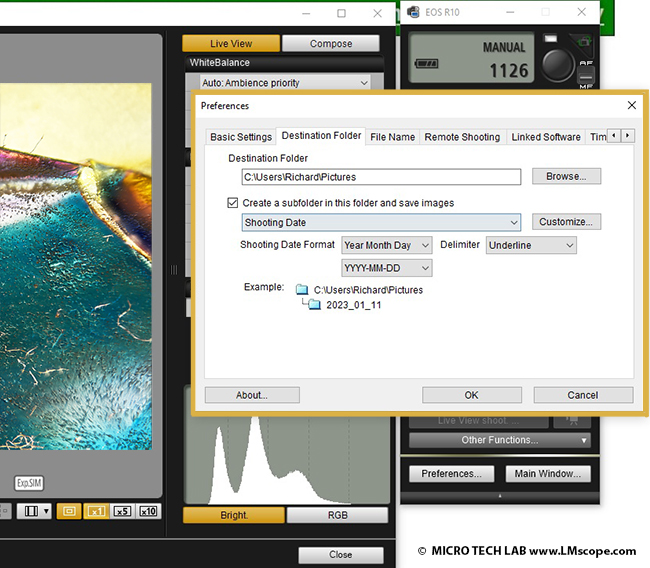
The magnifying function can be used to fine-tune the focal plane and make focus adjustments as required, and the remote shutter release and the possibility to capture directly to the hard drive are also very useful features – you don’t even need an SD card. The storage location where you want your images stored is selected in Explorer, and other information such as the recording time is checked regularly and synced with the computer’s clock.
In some cases, however, working with a computer is not possible, and this is where the camera’s fully-articulating display really comes in handy. The flexible design of the 3'' TFT LCD touchscreen gives you the freedom to adjust the screen in all directions to accommodate your working position. The touch function of the screen also makes it easy to control many of the camera’s features.

To display the live image on a large monitor, we recommend using the HDMI micro out terminal.

The HDMI settings can be changed in the camera menu (HDMI resolution).
Menu navigation is intuitive and easy, since the camera features Canon’s customary index card layout.
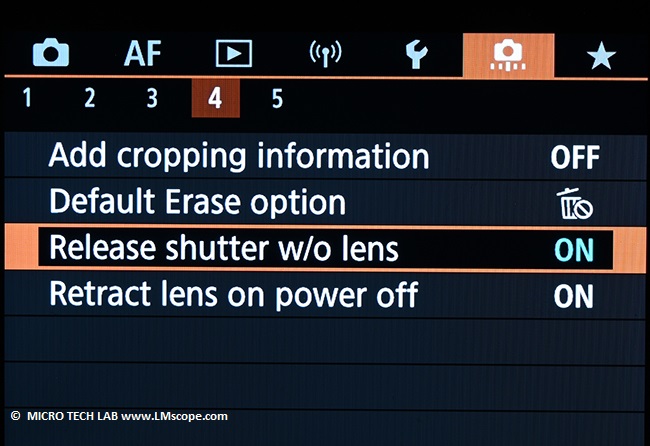
Before starting work, the settings must be adjusted to enable the camera to shoot without the original lens, since it is attached directly to our adapter solution. This setting can be enabled in the menu:
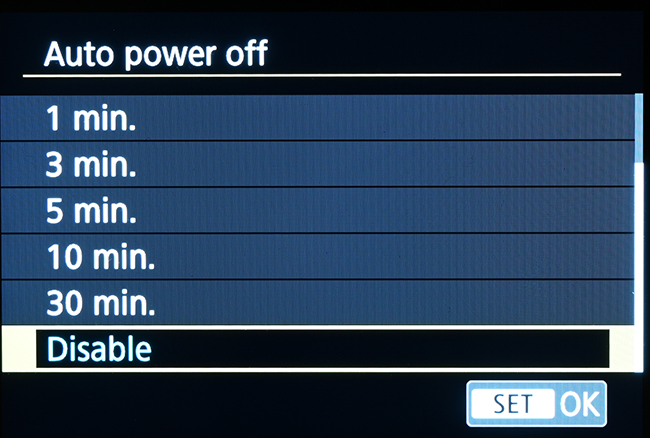
It is also advisable to disable the auto power save mode to prevent the camera from shutting down at inappropriate times, for example when it is used for presentations or longer shooting sessions.
To set the camera to save images directly to the computer, you need to enable the “shoot without card” option in the menu:
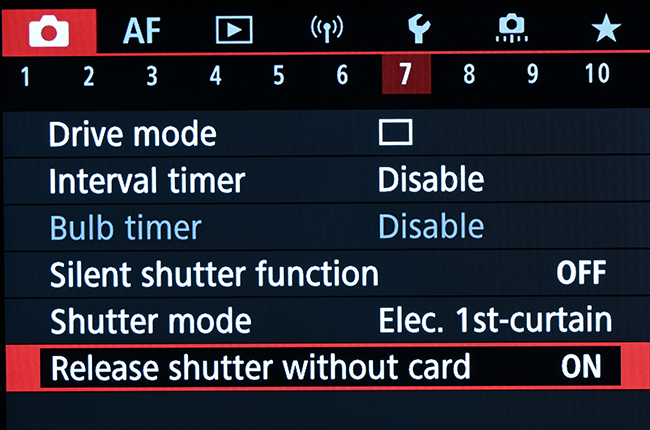
Now we need to adjust some shooting settings. The second menu page provides access to several important settings such as exposure level, ISO or HDR mode.
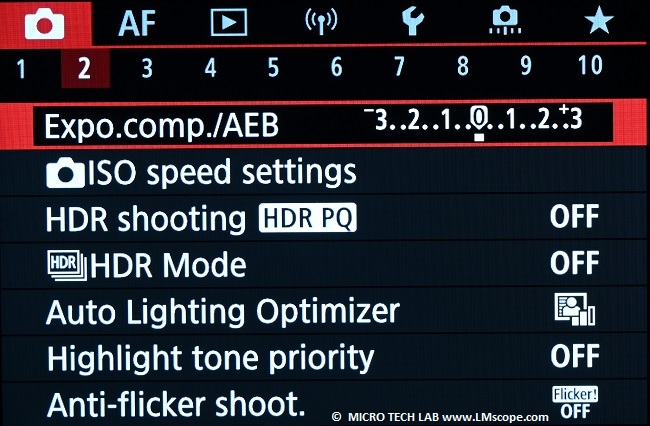
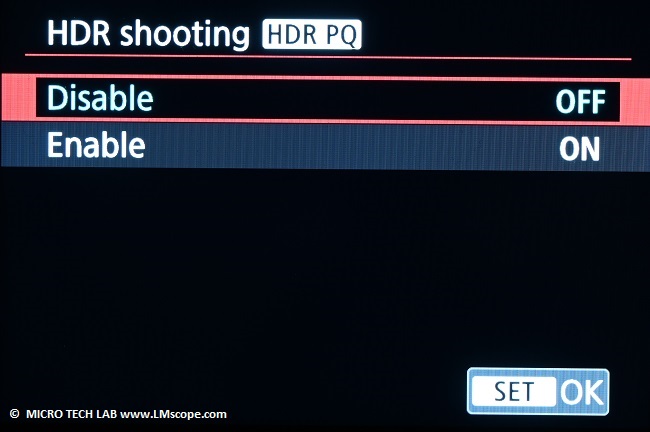
With the R10’s in-camera HDR imaging function (several images at different exposures are combined into one “super” image), the captured images can be made even more appealing.

White balancing improves the image quality another notch. The usual options (auto, semi-auto and manual) are available:

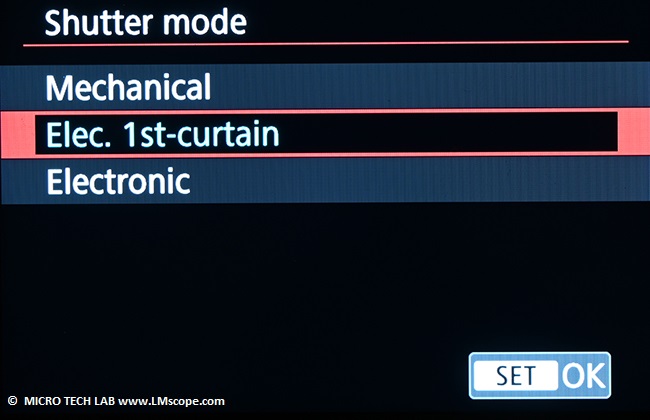
To avoid camera shake caused by the mechanical shutter, enable the electronic shutter and/or the “Silent shutter function”:
Conclusion: The EOS R10 can definitely hold its own against the comparable camera models of competitor brands. The fact that there is no time limit for video recording and the extremely fast sensor are highlights that should place the EOS R10 on the radar of novice and advanced photomicrographers alike.
20.09.2022Photography:
Fitting the microscope to digital single-lens reflex (DSLR), mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILC ), digital single-lens mirrorless (DSLM) or C-mount cameras is easy with our LM digital SLR adapters, which feature a plan achromatic optical system. Our products make it possible to capture top-quality microscope images. To help you select the adapter that is right for your camera, we have set up an online configurator on our website. You can also email us – ideally with attached photographs of your microscope.
Modern DSLR and single-lens mirrorless (DSLM) offer the latest technology and are generally very well suited for microscopy applications. Most of them can be controlled remotely via PC/Mac. Because of their high sales volumes, they offer an excellent price/performance ratio compared to special-purpose microscope cameras.
Features of top DSLR and single-lens mirrorless cameras (DSLM):
- Large, powerful full-frame sensors (36 x 24 mm)
- Sensor resolution of 61 megapixels or 240 megapixels with Pixel Shift technology
- High light sensitivity (ISO 400,000+)
- Extensive dynamic range (up to 15 aperture stops/f-stops)
- Short exposure times (1/8000 second) up to 1/32,000 seconds using the digital shutter
- 4K Ultra HD or 8K Ultra HD video function
- Live video capture on external monitors in ultra HD quality
In most cases, these cameras are significantly more powerful than microscope cameras with smaller sensors (1/2" or 2/3"). On our website you will find our current camera recommendations and a camera ranking which is specifically tailored to microscopy applications.